General information about screening
Epidemiological data
According to current cancer incidence data Serbia is on the 18th place in Europe and according to cancer mortality data on the second place. This clearly indicates the need for greater involvement in the prevention and early detection of cancer. Taking into account this data the Republic of Serbia is introducing organized cancer screening programs.
The most common malignancies in Serbia in 2012 were: breast cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, colorectal cancer and cervical cancer.
Cervical cancer in Serbia (Globocan 2012):
• standardized mortality rate was 7.7 per 100,000;
• according to the cervical cancer mortality data, Serbia is in third or fourth place among European countries;
• two-thirds of all cases are detected after the early invasive stages;
• more than 600 women are dying from cervical cancer each year.
Breast cancer in Serbia (Globocan 2012):
• standardized mortality rate was 22 per 100,000;
• breast cancer is the third leading cause of death among women older than 45 years;
• breast cancer is diagnosed in one in twelve women;
• 70% of people with diagnosed breast cancer have changes in breast bigger than 2 cm;
• more than 2000 women are dying from breast cancer every year
Colorectal cancer in Serbia (Globocan 2012):
• standardized mortality rate was 16.6 per 100,000;
• the second cause of cancer death in men, and the third cause of cancer death in women;
• mortality rate in men is higher by 15% and in women by 19% of the mortality rates in the EU;
• more than 3,000 men and women die from colorectal cancer every year
Organized screening
Screening programs significantly reduce mortality from cervical, colorectal and breast cancer. Screening is the identification of previously undetected disease, using screening tests in apparently healthy, asymptomatic target population. The goal of breast cancer screening is to reduce mortality, while the organized screening of cervical and colorectal cancer is reducing both incidence and mortality.
Organized screening represents invitation of the target population for testing and interpretation of screening tests followed by strict quality control and reporting. Organized screening is done in cycles of several years (2 or 3, depending on type of the screening), according to epidemiological and demographic data as well as human and financial resources.
Organized screening is organizationally very demanding and complex process. It is necessary to introduce it gradually in accordance with the provision of all necessary material and financial conditions as well as the training of health professionals.
Screening test
Screening test is used for early detection of disease. The test must be highly sensitive, specific and easy to apply. Screening test for early detection of cervical cancer is cytological smear of the cervix, for colorectal cancer it is immunochemical test for occult blood in the stool (iFOB test) and colonoscopy and for breast cancer it is mammography.
Collecting data on screening
Collection of certain data in screening process is very important , in order to display quality screening results in terms of effectiveness efficiency and the cost of the screening. The data are collected and registered at the time and place they occur, completing the protocol (clinical pathway) for each participant individually in screening. Summary periodic data are forwarded to the Institute of Public Health and the Cancer Screening Office as reporting form, either electronically or on paper. For the success of screening it is necessary to clearly define responsibilities of all individuals in each stage of the screening and to achieve good cooperation between all stakeholders - from health centers, institutes of public health, health care institutions on the secondary and tertiary level to the Health Insurance Fund and the Ministry of Health.
Participants in screening• Ministry of Health; • Health Insurance Fund; • Republican Expert Commission; • Institute of Public Health of Serbia "Dr Milan Jovanovic Batut"; • Cancer Screening Office • regional Institute of Public Health; • primary health care center; • health care institution of the secondary / tertiary level; • local community; • media. |
Primary health center is conducting screening in the territory for which it is established. The Cancer Screening Office coordinates, organizes, monitors and evaluates the implementation of screening and provides training and technical assistance to other participants in organized screening.
Start of organized screening in Serbia.
The Republic of Serbia has started the gradual introduction of organized screening for cervical, colorectal and breast cancer since 2012.
 |
|
Cervical cancer screening |
|
|
Cervical cancer screening is carried out on the territory of the Republic of Serbia as organized decentralized program. |
Target population: women, 25 to 64 years of age.
Coverage of the population: the aim is to include at least 75% of the target population.
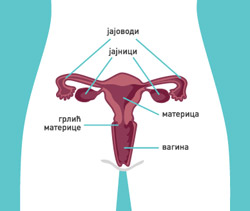
Screening cycle: 3 years (after two negative findings in the first two years).
Screening test: Pap test (Papanikolau) - cytological smear of the cervix.
Interpretation of tests: cytoscreeners and supervisors for positive Pap smears in accredited cytolaboratories.
The completion of the screening cycle: screening for cervical cancer ends with normal Pap test and in the case of abnormal Pap test results, colposcopy or HPV test are performed, as triage test, if possible.
Diagnosis, treatment: hospitals and clinical centers, according to guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of cervical cancer (2012).
Results Collection: primary health centers
In accordance with guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of cervical cancer 2012/2013., personal gynecologist informs participant in screening about results of screening test and determining the dynamics and content of follow-up, including referral for further diagnostics.
Data Collection and reporting: primary health centers, hospitals, regional Institutes of Public Health, Cancer Screening Office and Ministry of Health.
 |
|
Breast Cancer Screening |
|
|
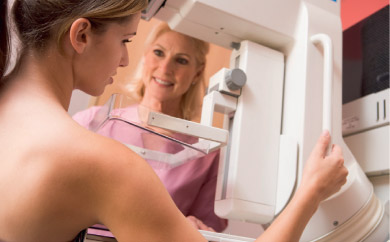
Breast cancer screening is carried out on the territory of the Republic of Serbia as organized decentralized program. |
Target population: women, 50 to 69 years of age.
Coverage of the population: the aim is to include at least 75% of the target population.
Screening Cycle: 2 years.
Screening tests: screening mammography.
The interpretation of mammographic images: double, performed by two independent, trained radiologists.
The completion of the screening cycle: The screening process ends with negative result of mammography image or after additional procedures (ultrasound breast examination and targeted screening mammography) when the result of mammographic image is positive.
Further diagnostic procedures and monitoring: primary health care centers, hospitals, clinical centers, institutes.
Results Collection: primary health centers
In accordance with guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer 2012/2013, personal gynecologist with the recommendation of radiologists informs participant in screening about results of screening test and determining the dynamics and content of follow-up, including referral for further diagnostics.
Data Collection and reporting: primary health centers, hospitals, regional Institutes of Public Health, Cancer Screening Office and Ministry of Health.
 |
|
Colorectal Cancer Screening |
|
|
Colorectal cancer screening is carried out on the territory of the Republic of Serbia in the form of organized decentralized program. |
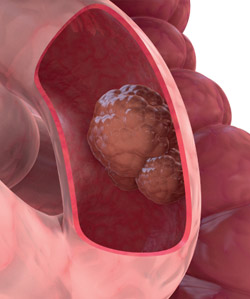 Target population: men and women, 50 to 74 years of age.
Target population: men and women, 50 to 74 years of age.
Coverage of the population: the aim is to include at least 75% of the target population.
Screening Cycle: 2 years.
Screening test: immunochemical test (iFOB test).
Interpretation of tests: laboratory at the primary health care center (trained laboratory technicians / nurses).
Additional procedures for positive iFOB tests: colonoscopy.
The completion of the screening cycle: The screening process ends with negative iFOB test and in the case of a positive iFOB test - colonoscopy and hystopathological findings after the biopsy.
Further treatment and monitoring: hospitals and clinical centers.
Results Collection: primary health centers
In accordance with guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer 2012/2013., personal doctor is informs participant in screening about results of screening test and determining the dynamics and content of follow-up, including referral for further diagnostics.
Data Collection and reporting: primary health centers, hospitals, regional Institutes of Public Health, Cancer Screening Office and Ministry of Health.
